Do you know what this Computer Processor is? Whenever we talk about a computer, the matter of Processor comes in our mind. A computer is not possible without a processor. Yes, it is right that if a processor’s efficiency is low, some of it is more. But having a processor is mandatory for all computers. This Processor has many names such as CPU, central Processor, and microprocessor CPU i.e., its full form is Central Processing Unit. Like this, it is the brain of a computer that keeps an eye on all the activities. He handles all these instructions that he gets from hardware and software. If seen, it is a hardware that does all the calculations very quickly, when it receives some input, then processes it, and after doing some calculation, the result is out.
But do you know how this small thing alone processes so much information? Today, we want to give some information to you in this article, What is Processor and how it works. Then what is the delay? Let’s start.
What is the Processor?
Table of Contents

The Processor is a very important part of the computer. It is also called the brain of the computer. This is because the news of all the activities happening inside the computer is near it, so it says that it controls all these things. It can process trillions of Calculation at a time. By understanding the interpretation between software and hardware, it processes and gives us the output. It is inside all the devices like Mobile, Tablets, Personal Computers, Laptops. It is also known as CPU.
It is a square-shaped device in appearance, from which many metallic, short, and rounded connectors are lowered out. It is attached to the CPU’s Socket itself. After running for a long time, it becomes slightly hot, that is why a heat sink and fan is put on it to release the heat. It is a very delicate thing, due to which it is carefully placed in the motherboard. They come in many types, such as Intel’s Processor i3, i5, and i7.
History of Processor
Intel first designed the first single-Chip Microprocessor in the world in 1971. It was invented by Intel’s three Engineers Federico Faggin, Ted Hoff, and Stan Mazo. This chip, named Intel 4004 Microprocessor, was designed to ensure all the processing functions like CPU, Memory, and Input and Output Control were placed in a single chip. Gradually, innovations occurred with time, which led to a lot of changes in computer design. Their working capacity increased, and their size decreased. Intel is now the leader of the world of Processor. They make the Processor of every variety according to the needs of the people.
What does CPU do
The CPU has three primary functions. First, it takes information, second, it does some operation on it, and third, it gives results after Calculation. But to do these three processes, it has to use some key components. ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit) subtraction and addition in binary. Along with this, they also do some logical operations like AND, NOT and OR, to help the CPU. Control Circuit directs data traffic from CPU to slower Input / Output devices so that that traffic can be exchanged. The Memory Management Unit monitors the flow of data to and from Memory.
Type of CPU
In the last few years, many types of CPUs have been invented. As time went on, so did new CPUs as per the requirement. Earlier the number was used to identify the Processor. For example, the Intel 80486 (486) processor is much faster than the 80386 processor. Ever since Intel launched the Pentium Processor (technically these are 80586), the processors have been named after them, such as Athlon, Duron, Pentium, and Celeron.
Nowadays, their architecture has changed along with the name, with the use of processors with only two types of architecture, it is now used quite a bit like 32 Bit and 64 Bit. Due to this architecture, now the speed and capacities of the Processor have also increased significantly. Processors such as AMD Opteron series and Intel Itanium, Xeon Series, are used in servers and high-end stations. And if we talk about small devices like Smart Phones and Tablets, then they use ARM Processor. These processors are smaller in size than usual, they require less power, and they produce very less heat.
What is the clock speed of the Processor?
This clock speed is also called clock rate and Processor speed. Clock speed is called the speed at which the Microprocessor executes each instruction or each vibration of the clock. Because the CPU needs a fixed number of clock ticks or cycles to run each direction, so the faster your clocks rate, the faster your CPU will be, or the quicker your Processor can execute instructions.
Clock speeds are measured in MHz, 1 MHz means 1 million cycles per second or GHz, 1 GHz means 1 thousand million cycles per second. In a general sense, then the higher CPU speed, the better your computer will perform. Computer speed also depends on other components such as RAM, hard drive, motherboard, and several processor cores (such as dual-core or quad-core).
This CPU speed shows how many calculations it can do in 1 second. The higher the speed, the more calculations it can perform, which will make your computer run faster. Different brands of computer processors are available in the market, such as Intel and AMD, but all of them follow the same CPU speed standard, to know which speed a processor runs.
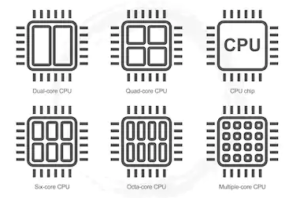
What is Core in Processor?
Processors have different cores according to their capacity. A typical processor has a single-core, ie, it is a single CPU. The Dual-Core processor consists of two processor circuits with two identical frequency. It can work at double speed as compared to Single Core Processor that too easily.
Currently, there are many different Core Processors available in the market, such as-
2 Core in Dual Core
4 Core in Quad Core
6 Core in Hexo Core
8 Core in Octa-Core
10 Core in Deca Core
The more Core the Processor, the more successfully it can complete multitasking.
How Processor Works
The Processor’s design is much more complicated than the standard design, and they vary significantly from company to company; even one model is quite different from the other. The Processor of two companies like Intel and AMD is in high demand in the market. These two companies are always engaged in trying to make how to improve the performance of the Processor by using less space and energy. But despite having so many architectural differences, the Processor mainly has to go through four processes, and only then can they process the instructions. These four processes are fetched, decode, execute, and write-back. Now I will tell you about all these processes.
1. Fetch
Fetch as if it means bringing something. Here the Processor retrieves the core instructions that remain in waiting in Memory. But in today’s Modern Processor, usually, those instructions are already waiting in the Processor Cache. There is an area in the Processor called Program Counter, which acts as a bookmark, informing the Processor about where the last instruction ended and where the next one started.
2. Decode
Once the instruction Fetch is done, then the next process is to decode it. There are many areas of a processor core in an instruction such as arithmetic and which the processor core has to recognize. There is also something in each part called Opcode, which tells the Processor what to do by using that instruction. Once the Processor acknowledges what he has to do, he does everything on his own.
3. Execute
In this step, the Processor knows what he has to do, and he makes him executive. What happens here depends on what Processor Core area comes in use and what information is put into it. For example, the Processor uses ALU to perform an arithmetic operation. It is believed that this operation takes place within ALU. This unit is connected to other inputs and outputs so that it can simplify its work and finally give us our results at the right time.
4. Writeback
This Aakir step can also be called, as its name is, its work is also the same, which places the result of all the three earlier work done in Aqir in Memory. To find out where the output has gone in Aakir, it depends on which application is running at that time. But it is usually in the register of the Processor itself because it is very much needed, then it is kept here for quick access.
This entire process is called Instruction Cycle. As we are progressing, we also have better processors, which are very fast and powerful. Our CPU is designed in such a way that it divides many tasks so that it can process as quickly as possible. And with new inventions, it seems likely.
Best Processor Company
1. Intel
2. AMD
Buy Here Best Processor- Click Here
Conclusion
Shortly, we will get to see an even better Processor. Nowadays, all the Processors’ companies are paying more attention to designing such processors in a short time that can be operated in less space and less power. And it should be more efficient. If we compare the processors of earlier times with today’s design, then we have become successful in this mission to a great extent. Hopefully, we will be able to create even more efficient processors in the future.
I sincerely hope that I have given you complete information about what the is Processor and how it works, and I hope that you guys have understood this computer term. I request all of you readers that you, too, should share this information in your neighborhood, relatives, and friends, so that we will have awareness among us and everyone will benefit a lot from it. I need your support so that I can convey more new information to you.
It has always been my endeavor that I always help my readers or readers from all sides, if you people have any doubt of any kind, then you can ask me irresponsibly. I will try to solve those Doubts. If you like this article what is Processor and how it works, please tell us by writing a comment so that we too have a chance to learn something from your ideas and improve something. To show your happiness and excitement about my post, please share this post on social networks such as Facebook, and Twitter, etc.